
Gout is a painful type of inflammatory arthritis that affects many people around the world. It causes sudden and severe pain, often in the big toe or other lower limbs. This pain can make it hard to walk or even stand.
The main cause of gout is too much uric acid in the body. This leads to the formation of sharp crystals that gather in the joints. These crystals cause inflammation, leading to swelling, redness, and a lot of discomfort.
Anyone can get gout, but some factors increase the risk. These include genetics, age, gender, and lifestyle choices. Men over 40 are more likely to get it. High blood pressure, kidney disease, and obesity can also make it more likely.
To diagnose gout, doctors look at symptoms, medical history, and test uric acid levels in blood or joint fluid. Once diagnosed, managing gout involves medication and lifestyle changes.
Managing gout means relieving pain during attacks and preventing more flare-ups. Doctors often prescribe NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids for pain and inflammation. Long-term treatments aim to lower uric acid levels with medications like xanthine oxidase inhibitors and uricosurics.
Eating right is key to managing gout. This means eating less of high-purine foods like organ meats, seafood, and alcohol. Increasing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy can help.
To prevent gout flare-ups, make lifestyle changes. Keep a healthy weight, drink plenty of water, exercise often, and avoid too much alcohol. These steps can reduce how often and how bad gout attacks are.
Key Takeaways:
- Gout is an inflammatory arthritis condition characterized by intense joint pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
- Excess uric acid in the body leads to the formation of sharp crystals that collect in the joints, triggering gout flares.
- Gout can be diagnosed through a combination of symptom evaluation, medical history, and laboratory tests.
- Treatments for gout focus on reducing pain during flare-ups and preventing future attacks through medication and lifestyle changes.
- A gout-friendly diet can help manage the condition by limiting purine-rich foods and increasing consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy.
What is Gout and Who Gets It?
Gout is a type of arthritis that can happen to anyone. It causes sudden, severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in one or more joints. The big toe is often affected, but other joints like the ankle, knee, elbow, wrist, or fingers can also be involved.
The main cause of gout is the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is a waste product that gets dissolved in the blood and then removed by the kidneys. But if there’s too much uric acid or the kidneys can’t get rid of it, crystals form and cause gout symptoms.
Not everyone gets gout, but some people are more likely to have it. Knowing who’s at risk can help prevent it:
- Genetics: If your family members have gout, you might get it too.
- Age and Sex: Men over 40 and postmenopausal women are more likely to get gout due to hormonal changes.
- Diet: Eating foods high in purines, like red meat and seafood, can raise uric acid levels and lead to gout.
- Medical Conditions: Being overweight, having high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, or metabolic syndrome increases gout risk.
- Medications: Some drugs, like diuretics for high blood pressure, can affect uric acid levels and cause gout.
| Gout Risk Factors | Brief Explanation |
|---|---|
| Genetics | Family history of gout increases the risk. |
| Age and Sex | Gout is more common in men over 40 and postmenopausal women. |
| Diet | Foods high in purines and sugary drinks can raise uric acid levels and trigger gout. |
| Medical Conditions | Conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, and metabolic syndrome raise gout risk. |
| Medications | Some drugs, such as diuretics, can affect uric acid levels and cause gout. |
Knowing the risk factors for gout helps in managing it better. By eating right, staying at a healthy weight, and taking your medicines, you can lower the chance of gout attacks and improve your life quality.
Next, we’ll look into how gout is diagnosed, which helps in starting the right treatment.
Diagnosing Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden and severe pain in the joints. Doctors use several methods to diagnose it, including:
- Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and past health to understand your condition. They’ll want to know about your diet, lifestyle, and any medicines you take.
- Physical Examination: In a physical exam, your doctor will check the affected joints for redness, swelling, and tenderness. They’ll also check how well you can move the affected joints.
- Joint Fluid Analysis: To confirm gout, your doctor will analyze fluid from the affected joint. They’ll use a needle to take the fluid, which is then checked under a microscope. Finding urate crystals in the fluid confirms gout.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests check your uric acid levels. High levels don’t always mean you have gout, but they help confirm it with other signs.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays or other scans might be used to rule out other conditions. They check the joint’s health and look for urate crystals.
Diagnosing gout can be tricky because its symptoms can look like other joint problems. Doctors use a mix of these methods to make sure they diagnose it correctly and plan the right treatment.
| Diagnostic Methods | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Fluid Analysis | – Confirms the presence of urate crystals – Highly specific for gout diagnosis | – Invasive procedure – Requires experienced personnel – May not always be feasible or available |
| Blood Tests | – Measures uric acid levels – Provides supportive evidence for gout diagnosis | – Elevated uric acid levels don’t confirm gout diagnosis alone – Normal uric acid levels don’t exclude gout diagnosis |
| Imaging Studies | – Helps rule out other conditions – Assesses joint damage and urate crystal accumulation | – Limited ability to visualize early-stage gout – Not a definitive diagnostic method for gout |
If you have gout symptoms, seeing a doctor is key to getting the right diagnosis and treatment. Early action can help ease symptoms and prevent future attacks.
Treating Gout
Understanding how to treat gout is key to managing it. Gout can’t be cured, but there are ways to ease symptoms and prevent attacks. Medical treatments and lifestyle changes can help a lot.
Doctors often prescribe medications for gout. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help with pain and swelling. Corticosteroids can quickly reduce inflammation during a flare-up. Colchicine is used to stop gout attacks before they start.
Changing your lifestyle is also important. Keeping a healthy weight is crucial because being overweight can make gout worse. Losing weight through diet and exercise can lessen the severity of gout attacks.
Drinking less alcohol is another key change. Beer, in particular, can raise uric acid levels and cause gout. Cutting down or stopping alcohol can help manage gout better.
Eating right is also vital for gout sufferers. Foods high in purines should be eaten less because they raise uric acid. Focus on fruits, veggies, low-fat dairy, and whole grains instead.
The right treatment plan for gout varies by person. It depends on your health history and how severe your symptoms are. Always talk to a healthcare professional to get a plan that’s right for you.
To sum up, gout can’t be cured, but it can be managed well. With the right medications, lifestyle changes, and diet, you can reduce symptoms and prevent future attacks. This can greatly improve your life with gout.
Gout-Friendly Diet

Following a gout-friendly diet can help manage gout symptoms and reduce attacks. It means choosing foods wisely and avoiding those that can trigger gout. This approach can make a big difference.
Purines are found in some foods and break down into uric acid in the body. For people with gout, the body either makes too much uric acid or doesn’t get rid of it well. This leads to uric acid crystals forming in the joints.
So, which foods cause gout? Foods high in purines should be eaten in small amounts or avoided. These include:
- Red meat
- Organ meats (liver, kidneys, etc.)
- Seafood (anchovies, sardines, mussels, etc.)
- Alcohol, especially beer and spirits
Not all foods high in purines need to be cut out completely. Moderation is key. Small amounts of these foods won’t usually trigger gout attacks. But, it’s best to talk to your healthcare provider or a dietitian for advice tailored to you.
On the other hand, what are some purine-rich foods that you can include in a gout-friendly diet? Here are some low-purine foods you can enjoy:
- Fruits (except for citrus fruits)
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Low-fat dairy products
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas, etc.)
Hydration is also key for managing gout. Drinking enough water helps flush out uric acid and prevents crystals from forming.
Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial as being overweight increases the risk of gout and more frequent attacks. Regular exercise can help you stay at a healthy weight.
Remember, a gout-friendly diet is a long-term change, not a quick fix. By eating a balanced and nutritious diet, you can reduce flare-ups and improve your health and well-being.
| High-Purine Foods to Limit or Avoid | Low-Purine Foods to Include |
|---|---|
| Red meat | Fruits (except for citrus fruits) |
| Organ meats (liver, kidneys, etc.) | Vegetables |
| Seafood (anchovies, sardines, mussels, etc.) | Whole grains |
| Alcohol, especially beer and spirits | Low-fat dairy products |
| Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas, etc.) |
Managing and Preventing Gout Flare-Ups

Gout flare-ups can be very painful and disrupt your daily life. Luckily, there are ways to manage and prevent these flare-ups. This helps reduce joint pain and discomfort.
Following the medication plan your doctor gives you is key in managing gout. Your doctor might suggest NSAIDs or corticosteroids to lessen inflammation and ease pain. It’s important to take these medicines as told and finish the treatment fully.
Making lifestyle changes is also vital in preventing gout flare-ups. It’s important to avoid things that can trigger gout attacks. This means cutting down on alcohol, especially beer, and foods high in purines like organ meats, seafood, and red meat. Instead, eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products.
During a flare-up, there are things you can do to help yourself. Putting ice on the affected joint for 15 minutes can lessen pain and swelling. Also, resting the joint on a pillow can make you feel better. Try not to put weight or pressure on the joint if you can.
Regular exercise and keeping a healthy weight are key to preventing flare-ups. Doing low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can help your joints and lower the risk of flare-ups. Always talk to your doctor before starting any new exercise plan.
In summary, managing and preventing gout flare-ups requires a mix of medication, lifestyle changes, and self-care. Stick to your medication plan, avoid triggers, and make healthy choices. This way, you can reduce how often and how bad gout flare-ups are. It helps you live a more comfortable and active life.
Gout and Inflammatory Arthritis: Outlook and Prognosis
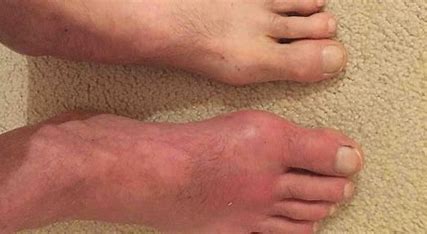
The outlook for gout and inflammatory arthritis depends on several factors. These include how severe the condition is, how well it’s managed, and overall health. Knowing about the long-term outlook and prognosis helps people manage their symptoms and improve their life quality.
Gout Outlook
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that often hits the big toe. If not treated or managed well, it can cause more flare-ups and tophi, which are hard lumps under the skin. But, with the right treatment and changes in lifestyle, most people can control their symptoms and cut down on flare-ups.
Handling gout means using medicines, changing your diet, and making lifestyle changes. Medicines like NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and colchicine help during flare-ups and can prevent more attacks. Eating a diet low in purines, drinking plenty of water, and keeping a healthy weight also helps lower the chance of flare-ups.
Inflammatory Arthritis Outlook
Inflammatory arthritis is a group of conditions marked by joint inflammation. This includes conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. The outlook for these conditions varies based on the specific condition and its severity.
Even though inflammatory arthritis is often chronic, new treatments have made things better for people. Finding out early, using targeted medicines, and making lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms, slow down the disease, and keep joints working well.
Working with doctors, like rheumatologists, helps create a treatment plan that fits your needs. This plan might include DMARDs, corticosteroids, and biologic therapies. Physical therapy, exercise, and using heat or cold can also help ease symptoms and improve joint function.
Joint Health and Prognosis
Gout and inflammatory arthritis can be ongoing, but managing symptoms and taking care of your joints can make a big difference. It’s key to work with healthcare professionals to make a treatment plan that suits you.
Staying active, keeping a healthy weight, and avoiding things that make symptoms worse can help your joints. Following your treatment plan, going to regular check-ups, and getting help for new or worse symptoms can lead to better outcomes and well-being.
| Gout | Inflammatory Arthritis |
|---|---|
| Mostly affects the big toe joint | Affects multiple joints in the body |
| Treatment includes medication, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications | Treatment involves medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments |
| Proper management can lead to fewer flare-ups and improved quality of life | Early diagnosis and treatment can slow disease progression and preserve joint function |
| Chronic condition; long-term management is necessary | Chronic condition; long-term management is necessary |
Living with Gout: Tips and Coping Strategies

Living with gout can be tough, but you can manage your symptoms well. Here are some tips and strategies to help you live with gout:
Follow a Gout-Friendly Diet
A diet low in purines is key for managing gout. Avoid foods like red meat, organ meats, and some seafood. Instead, eat fruits, veggies, whole grains, and low-fat dairy. Drinking plenty of water and limiting alcohol can also help prevent flare-ups.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight can make gout worse. Aim for a healthy weight with exercise and a balanced diet. Losing weight can lessen the number and severity of gout attacks.
Stay Physically Active
Exercise is good for everyone, even those with gout. Try low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling. These keep your joints moving and lower the chance of gout attacks. Always talk to your doctor before starting a new exercise plan.
Manage Stress
Stress can cause gout attacks. Find ways to relax, like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. Enjoy hobbies, spend time with family, and get support to reduce stress.
Take Prescribed Medications
Working with your doctor is crucial for managing gout. They may prescribe medicines to lower uric acid levels and prevent attacks. Always take your medicines as told and go to regular check-ups.
Seek Support
Gout affects you physically and emotionally. Don’t be afraid to talk to healthcare experts, like rheumatologists, who know about gout. They can offer advice, support, and tailored treatment plans. Joining support groups or online forums can also connect you with others who understand what you’re going through.
Managing gout means being proactive. By eating right, staying active, handling stress, and getting support, you can live well with gout.
Gout Myths Busted
Many people have wrong ideas about gout that have stuck around for a long time. It’s important to clear up these myths for better understanding and handling of the condition.
Myth 1: Gout only affects older individuals
Some think gout only hits older folks. While older people are more likely to get it due to metabolism and lifestyle changes, gout can happen to anyone. Sadly, more young people are getting it now.
Myth 2: Gout is caused by consuming too much protein
It’s a common belief that eating too much protein causes gout. While some high-protein foods can trigger gout in some, it’s mainly about uric acid buildup. This leads to gout symptoms. Genetics, medicines, and health conditions also play big roles in gout.
Myth 3: Gout can be cured by over-the-counter remedies
Some think gout can be fixed with things like cherry juice or apple cider vinegar. But, these natural remedies can only help with symptoms, not cure the condition. Managing gout well needs lifestyle changes, medicine, and doctor advice.
“Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” – Nelson Mandela
Myth 4: Gout is only a joint problem
Gout is often seen as just a joint issue. But it’s a bigger problem that can affect the kidneys and heart too. It’s key to know the risks and get the right medical help.
In short, it’s crucial to clear up these gout myths for better understanding and handling. Knowing the truth about gout helps people make smart health choices and prevent attacks.
Gout and Inflammatory Arthritis: Frequently Asked Questions
If you have gout or inflammatory arthritis, you might have questions about your condition and how to manage it. We’ll cover common questions about gout and inflammatory arthritis here. This will give you useful info and insights.
1. What is gout?
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis. It happens when uric acid crystals build up in the joints. This leads to sudden, severe pain, swelling, and tenderness.
2. Who is at risk of developing gout?
Anyone can get gout, but some people are more likely to. Risk factors include a family history of gout, being overweight, eating foods high in purines, drinking too much alcohol, certain health conditions, and some medications.
3. How is gout diagnosed?
To diagnose gout, doctors look at your medical history, do a physical exam, and run tests. They might check your blood for uric acid levels and use X-rays or ultrasounds to see if your joints are damaged.
4. What are the treatment options for gout?
Treatment for gout aims to ease pain, reduce swelling, prevent attacks, and lower uric acid levels. Doctors might prescribe NSAIDs, colchicine, corticosteroids, or medicines to lower uric acid. Making healthy lifestyle changes is also key.
5. Can dietary changes help manage gout?
Yes, eating right can help with gout. You should eat fewer foods high in purines and drink less alcohol. Increase your fruits, veggies, whole grains, and low-fat dairy to help manage gout attacks.
6. How can gout and inflammatory arthritis flare-ups be managed and prevented?
To manage and prevent flare-ups, stick to your medication and make lifestyle changes. Keep active, maintain a healthy weight, avoid foods and activities that trigger attacks, and manage any health conditions that cause inflammation.
7. What is the outlook for individuals with gout and inflammatory arthritis?
The outlook for gout and inflammatory arthritis depends on several things, like how severe it is, how well you follow your treatment, and your lifestyle. With the right care, many people can lead fulfilling lives despite their condition.
8. What are some tips and coping strategies for living with gout?
Living with gout can be tough, but there are ways to make it easier. Talk to your healthcare team, eat right, stay active, manage stress, avoid triggers, and get support from loved ones or support groups.
9. What are some common myths about gout?
There are many myths about gout. Some think it’s only caused by drinking too much alcohol or that it only affects older people. It’s important to know the facts to make informed health choices.
10. What are the latest research and advances in gout treatment?
Research on gout is ongoing to improve treatment options. Scientists are looking into new medicines and personalized treatments based on individual needs. This could lead to better ways to manage gout in the future.
We hope these answers help you understand gout and inflammatory arthritis better. Always talk to your healthcare provider for advice tailored to your situation and health history.
| Gout VS Inflammatory Arthritis | Gout | Inflammatory Arthritis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gout is a type of arthritis caused by uric acid crystals in the joints. | Inflammatory arthritis is a group of conditions where the immune system attacks healthy joint tissues. |
| Causes | Uric acid crystals build up because the body can’t break down uric acid well. | The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues. |
| Symptoms | Severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in joints, often in the big toe. | Pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited movement in multiple joints. |
| Treatment | Medicines for pain, inflammation, and lowering uric acid levels. Diet changes and weight management are also important. | Medicines to reduce the immune response and inflammation. Physical therapy, joint protection, and assistive devices may be recommended. |
| Prognosis | Most people with gout can manage the condition well and live active lives. | The outlook varies by condition and severity. Early diagnosis and treatment can help reduce joint damage and improve outcomes. |
Latest Research and Advances in Gout Treatment

The field of gout treatment is always getting better with new research and trials. These efforts aim to help patients feel better and manage their gout better. The latest studies have made big strides in understanding gout and finding new treatments.
New medicines are being developed to treat gout. Scientists and companies are working hard to find new ways to lessen gout symptoms and stop flare-ups. This is good news for people who haven’t found relief with current treatments.
“Gout is a complex inflammatory condition that requires a multifaceted approach to treatment. The latest research is shedding light on new strategies to better manage gout and improve the quality of life for patients.”
Researchers are also looking into new ways to treat gout. They’re focusing on therapies that target specific molecules and pathways involved in inflammation. This could lead to treatments that work better and last longer.
Studies now highlight the role of lifestyle changes in managing gout. Eating foods low in purines can help reduce attacks. Foods like vegetables, fruits, and whole grains are good choices. Avoiding foods high in purines can also help.
Exploring Future Possibilities
Looking to the future, research on gout treatment is exciting. Scientists are looking at new targets, like enzymes and parts of the immune system, that might be involved in gout. This could lead to more targeted treatments for gout patients.
Clinical trials are testing these new approaches. They involve people with gout, helping us learn more and make better treatment plans.
In conclusion, the latest research and advances in gout treatment bring hope. From new medicines to innovative treatments and understanding lifestyle changes, the future looks bright for gout patients. Continued research and teamwork between doctors, scientists, and patients will shape the future of gout treatment.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful type of inflammatory arthritis that many people face. But, with the right strategies, you can manage it well and lessen its effect on your daily life.
Working with healthcare experts, you can create a treatment plan that includes medicines, lifestyle changes, and self-care. This approach can lessen gout symptoms and stop flare-ups. It helps you live a full and active life.
Managing gout also means eating foods that are good for you. Choosing the right foods can lower uric acid levels in your body, which helps prevent gout. Also, living a healthy lifestyle, like keeping a healthy weight, exercising, and not drinking too much alcohol, supports managing gout.
In conclusion, even though gout can be tough, you’re not alone. With medical advice and proactive steps, you can take back control of your life. This way, you can lessen the effects of gout on your health and well-being.
FAQ
What is gout?
Gout is a painful arthritis type. It happens when the body has too much uric acid. This leads to sharp crystals forming in the joints.
What are the symptoms of gout?
Gout brings intense joint pain, swelling, redness, and less movement.
What causes gout?
Gout is caused by uric acid crystals building up in the joints. Factors that increase the risk include genetics, age, sex, diet, certain health conditions, and some medicines.
How is gout diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose gout by looking at symptoms, medical history, and doing tests. They might check for urate crystals in the joint fluid.
How is gout treated?
Treatment for gout aims to ease symptoms and prevent more attacks. Doctors often prescribe NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and colchicine.
Can gout be cured?
There’s no cure for gout, but treatment can control it and lessen symptoms.
Which foods cause gout?
Foods high in purines, like red meat, organ meats, seafood, and alcohol, should be eaten less or avoided to prevent gout attacks.
How can gout flare-ups be managed and prevented?
To manage and prevent gout flare-ups, use medication, make lifestyle changes, and take care of yourself. Always follow your doctor’s advice, avoid gout triggers, and use ice on the affected joint.
What is the outlook for gout and inflammatory arthritis?
Gout and inflammatory arthritis outcomes vary. They depend on the condition’s severity, management, and your health. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, many people with gout can control their symptoms and reduce flare-ups.
How can I live with gout and inflammatory arthritis?
Living with gout means making some lifestyle changes. This includes eating right, staying fit, managing stress, and taking your medicines as told by your doctor.
What are some common myths about gout?
Some believe gout is from eating too much protein or that it only hits older people. It’s key to know the facts to manage gout well.
Are there any latest research and advances in gout treatment?
Gout research is always moving forward. There are ongoing studies and trials on new treatments. This section will cover the latest in gout treatment, including new drugs, therapies, and future possibilities.
Source Links
- Gout – Symptoms and causes – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gout/symptoms-causes/syc-20372897
- Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Gout – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2014/1215/p831.html
- How Do I Know if my Joint Pain Is Gout? – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4755-gout






Leave a comment